In today’s digital landscape, data breaches have become a common and significant threat to organizations of all sizes. It is crucial for businesses to have robust data breach response strategies in place to effectively handle security incidents. In this article, we will explore the key components of an effective incident handling process and provide practical strategies for mitigating the impact of data breaches.
- Incident Response Plan: A well-defined incident response plan is the foundation of an effective data breach response strategy. It outlines the step-by-step procedures to be followed when a security incident occurs. Key elements of an incident response plan include:
- Clear roles and responsibilities of team members involved in incident response.
- Guidelines for identifying, classifying, and reporting security incidents.
- Communication protocols for internal teams, external stakeholders, and regulatory bodies.
- Procedures for evidence preservation, forensic analysis, and containment of the incident.
- Remediation and recovery actions to restore systems and prevent future incidents.
- Rapid Detection and Analysis: Early detection of a data breach is crucial for minimizing the impact. Organizations should implement robust monitoring and detection mechanisms to identify suspicious activities and anomalies in real-time. Key strategies include:
- Intrusion detection and prevention systems that monitor network traffic and identify potential threats.
- Log monitoring and analysis to detect unauthorized access attempts or unusual system behavior.
- Security information and event management (SIEM) tools that aggregate and correlate security events for timely detection.
- Advanced threat intelligence and analytics to identify emerging threats and vulnerabilities.
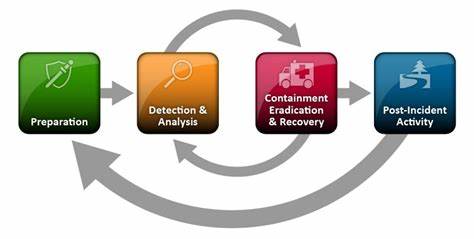
- Incident Containment and Damage Control: Once a data breach is detected, it is essential to contain the incident to prevent further damage and data exfiltration. Strategies for incident containment and damage control include:
- Isolating compromised systems or networks to limit the attacker’s access.
- Changing passwords, disabling compromised accounts, and revoking unauthorized privileges.
- Applying patches and security updates to vulnerable systems.
- Conducting forensic analysis to determine the extent of the breach and gather evidence for legal and regulatory purposes.
- Communication and Reporting: Timely and transparent communication is vital during a data breach. Organizations should have a well-defined communication strategy that includes:
- Internal communication channels to notify relevant stakeholders, including executives, IT teams, and legal departments.
- External communication protocols to inform customers, partners, regulatory bodies, and law enforcement agencies, as required by applicable regulations.
- Crafting clear and concise messages that provide accurate information about the incident, potential impact, and steps taken for remediation.
- Designating spokespersons or a crisis management team to handle media inquiries and manage public relations.

- Lessons Learned and Continuous Improvement: After a data breach incident, organizations should conduct a thorough post-incident analysis to identify gaps, vulnerabilities, and areas for improvement. Key steps in the lessons learned process include:
- Analyzing the root causes of the incident and identifying any weaknesses in security controls or processes.
- Reviewing the effectiveness of the incident response plan and making necessary updates.
- Conducting employee training and awareness programs to reinforce security best practices.
- Regularly testing and refining incident response procedures through tabletop exercises and simulations.
- Engaging with external cybersecurity experts and industry peers to gain insights and share knowledge.
Data breach incidents can have severe consequences for businesses, including financial losses, reputational damage, and regulatory penalties. By implementing effective incident handling strategies, organizations can mitigate the impact of data breaches and enhance their overall security posture. A proactive and well-prepared approach, coupled with continuous improvement and learning, is crucial in today’s rapidly evolving threat landscape. Remember, effective incident response is not just about responding to incidents but also about being prepared to handle them confidently and effectively.


Leave a Reply